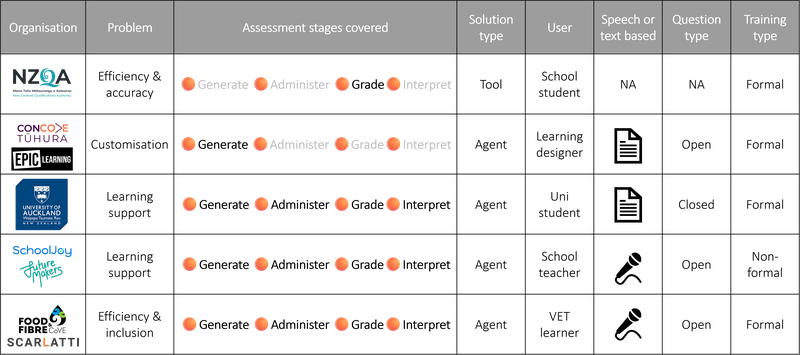
Before getting into AI for assessment – it may be worthwhile understanding the forms of solution that could exist for it. As mentioned in a previous article, AI can be used for assessment to generate tests, administer them, grade students, or interpret insights to provide additional support to users. However, the exact solutions used in different instances may not necessarily be a ‘chatbot’. Our impression is that some terms are currently being used interchangeably. Below, we offer an attempt at definitions:
AI Platform
An AI platform is an application that brings together a range of AI services in one place. Through these platforms, users can build, deploy, and manage AI tools, chatbots and agents. Examples of AI platforms include Microsoft Azure AI, Google Cloud Platform, or the University of Sydney’s Cogniti platform, which is specifically for educators to develop their own agents (see more about this in our earlier article).
AI Tool
AI-powered tools are tools designed to perform a specific function or set of tasks using AI algorithms. It will often involve a user interface with buttons, menus, or other forms of structured input. In some cases, it may simulate a human-like conversation with the user, for example, a quiz generator.
Chatbot
A generic pre-large language model chatbot performs pre-defined functions and answers common questions. Unlike advanced AI systems (e.g., ChatGPT), pre-LLM chatbots are often rule-based or use natural language processing to generate structured responses, for example, a website’s ‘help desk’ chatbot.
AI Agent
By comparison, AI agents (confusingly also being an AI chatbot by many in early 2025) are designed to simulate human-like conversations and handle multiple tasks. Agents do so by focusing on real-time interactions and responding dynamically to questions or prompts. It can provide information, perform actions, or guide users interactively, for example, Siri by Apple or Alexa by Amazon.
 Phoebe Gill
Phoebe Gill